BLOG > Publications & Citations > BCL2 drives castration resistance in castration-sensitive prostate cancer
Authors: Hirani, Rahim et al.
Source: Cell Reports, Volume 44, Issue 6, 115779.
We're thrilled to share insights from a genuine study entitled "BCL2 drives castration resistance in castration-sensitive prostate cancer by orchestrating reciprocal crosstalk between oncogenic pathways" published in Cell Reports by Rahim Hirani et al.
Congratulations to all the authors on this excellent article!
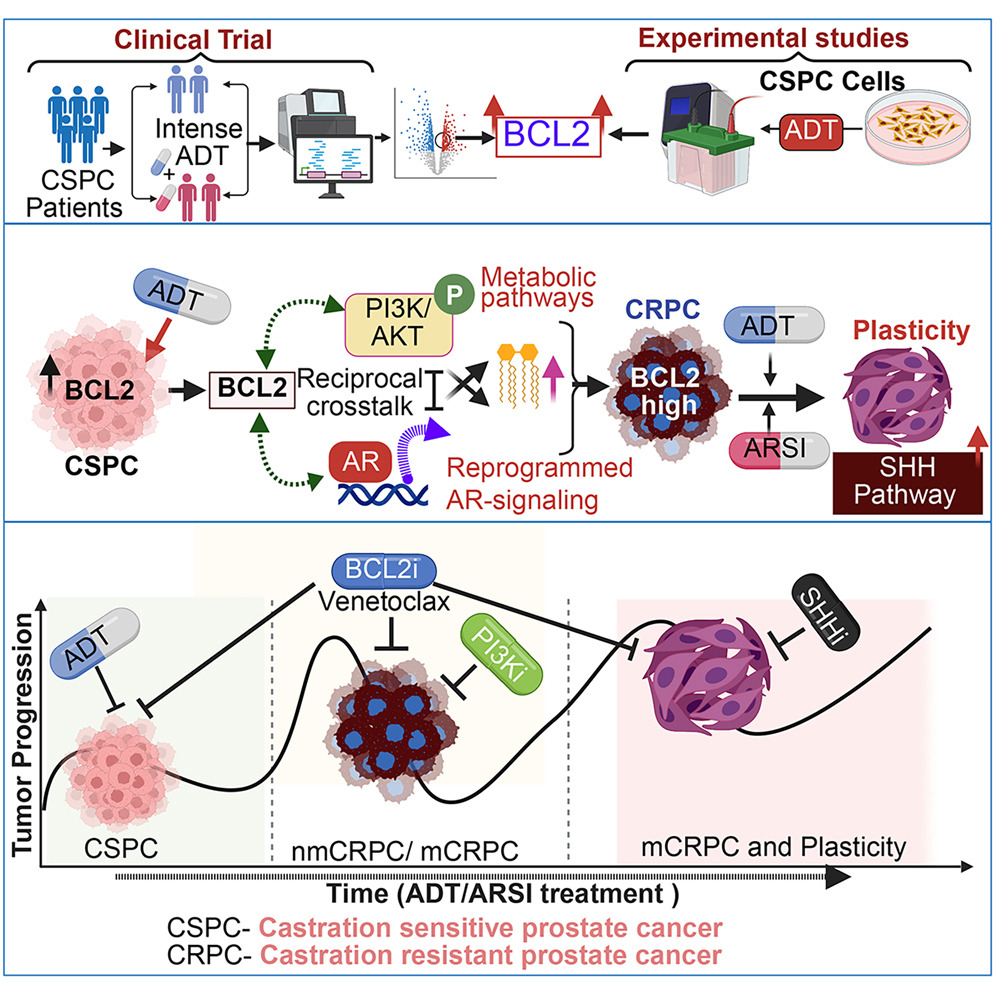
This study identifies how androgen-deprivation therapy (ADT) increases BCL2 expression in castration-sensitive prostate cancer (CSPC) cells, which then orchestrates a complex crosstalk with AR and PI3K signaling pathways, ultimately contributing to the development of lethal castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC).
A key aspect of this investigation involved the precise use of molecular tools to understand BCL2's impact. Researchers generated lentiviral vectors to encode BCL2 and BCLXL, which were then utilized to infect LNCaP cells with the crucial assistance of our LentiBlast Premium Transduction Enhancer.
This method enabled the stable overexpression of BCL2 in these cells, allowing for rigorous study into how BCL2 overexpression influences AR signaling and contributes to ADT resistance, providing profound insights into CRPC progression.
The findings highlight that a BCL2 inhibitor, Venetoclax, was effective in delaying the ADT-induced emergence of CRPC from CSPC. Moreover, combining BCL2 inhibitors with AR inhibitors (like enzalutamide) demonstrated synergistic effects, enhancing growth inhibition and delaying resistance in preclinical models. The research also revealed that BCL2 overexpression under prolonged ADT leads to lineage plasticity and activates the Hedgehog signaling pathway, suggesting further therapeutic targets.
This work provides strong rationale for exploring BCL2-targeted combination therapies to potentially prevent or delay the transition from CSPC to CRPC.
Read the article See our LentiBlast Premium