BLOG > Publications & Citations > Growth factor de-sialylation controls glycolipid-lectin-driven endocytosis
Authors: MacDonald, E., Forrester, A., Valades-Cruz, C.A. et al.
Source: Nat Cell Biol 27, 449–463 (2025).
We are delighted to share insights from a recent study entitled "Growth factor-triggered de-sialylation controls glycolipid-lectin-driven endocytosis" published in Nature Cell Biology by Ewan MacDonald et al:
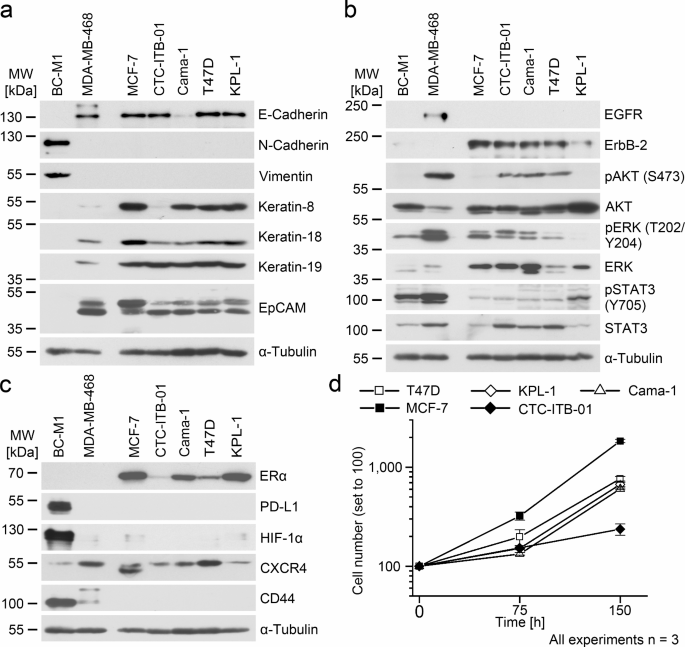
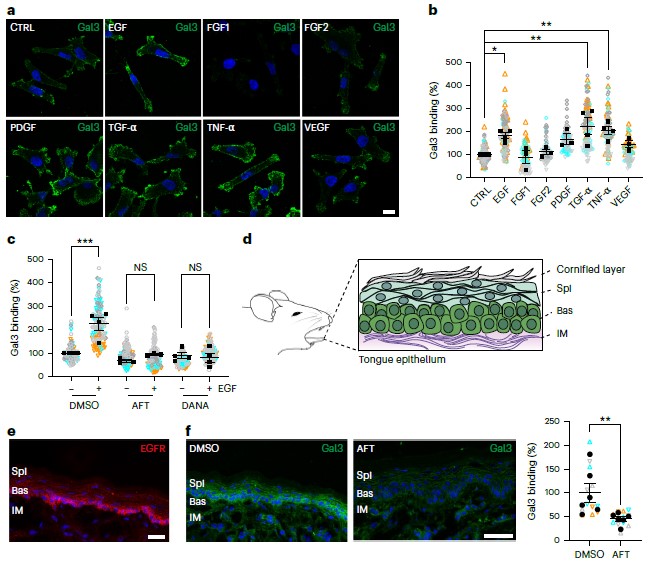
"Glycolipid-lectin-driven endocytosis controls the formation of clathrin-independent carriers and the internalization of various cargos such as β1 integrin. Whether this process is regulated in a dynamic manner remained unexplored. Here we demonstrate that, within minutes, the epidermal growth factor triggers the galectin-driven endocytosis of cell-surface glycoproteins, such as integrins, that are key regulators of cell adhesion and migration. The onset of this process—mediated by the Na+/H+ antiporter NHE1 as well as the neuraminidases Neu1 and Neu3—requires the pH-triggered enzymatic removal of sialic acids whose presence otherwise prevents galectin binding. De-sialylated glycoproteins are then retrogradely transported to the Golgi apparatus where their glycan make-up is reset to regulate EGF-dependent invasive-cell migration. Further evidence is provided for a role of neuraminidases and galectin-3 in acidification-dependent bone resorption. Glycosylation at the cell surface thereby emerges as a dynamic and reversible regulatory post-translational modification that controls a highly adaptable trafficking pathway."
Congratulations to all authors for this great article.
Our Lullaby Transfection Reagent was used for gene silencing in HeLa cells with siRNA.
Read the article See our Lullaby