BLOG > Publications & Citations > Concentration-dependent anti-inflammatory effects of BHB on microglia
Authors: Garcia Chase et al.
Source: Frontiers in Aging, Volume 6 - 2025.
We're delighted to share insights from a recent study entitled "Beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) elicits concentration-dependent anti-inflammatory effects on microglial cells which are reversible by blocking its monocarboxylate (MCT) importer" published in Frontiers in Aging by Garcia Chase et al:
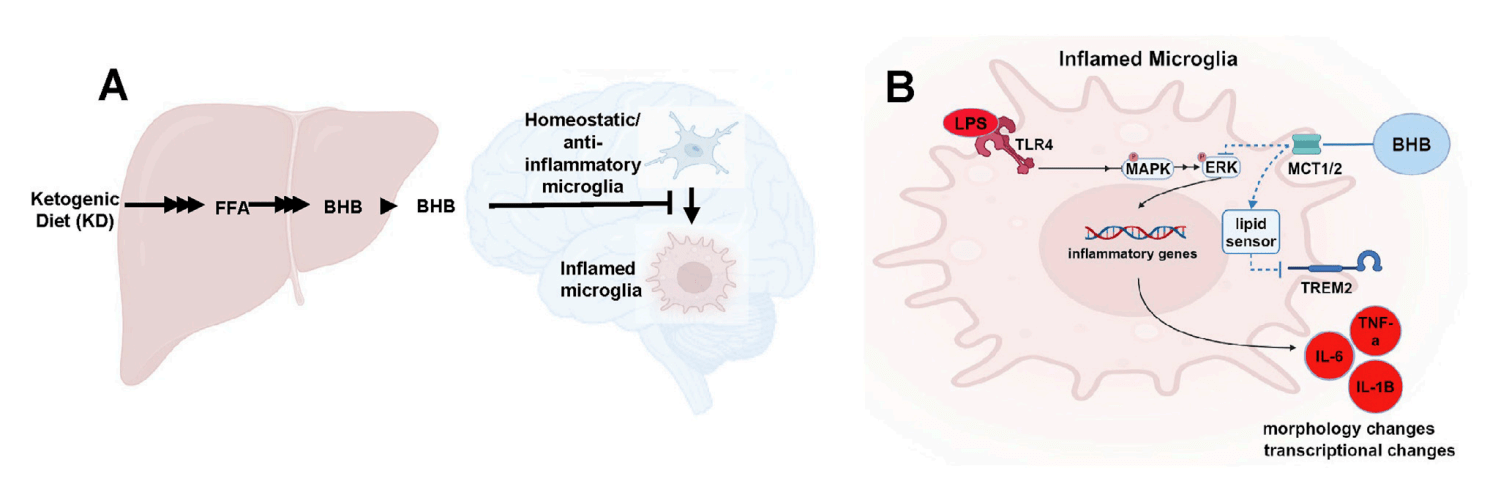
They uncovered key mechanisms behind the ketogenic diet's benefits for memory and longevity, demonstrating how beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) exerts significant concentration-dependent anti-inflammatory effects on microglial cells.
Their research, focusing on BV2 microglia, showed BHB reduces inflammatory responses and that these actions are dependent on its entry into cells via monocarboxylate transporters (MCTs).
Congratulations to all authors for this great article.
Our Glial-Mag Transfection Reagent was used to perform siRNA knockdown experiments targeting MCT1/2.
This allowed the team to prove that blocking BHB's cellular uptake reversed its anti-inflammatory effects.
Its high transfection efficiency, low toxicity, and, critically, lack of inflammatory activation made Glial-Mag a suitable choice for sensitive microglial studies.
Read the article See our Glial-Mag