BLOG > Publications & Citations > ITCH regulates Golgi integrity and proteotoxicity in neurodegeneration
Authors: Qiwang Xiang et al.
Source: Sci. Adv.11,eado4330 (2025).
We are delighted to share insights from a recent study entitled "ITCH regulates Golgi integrity and proteotoxicity in neurodegeneration" published in Science Advances by Qiwang Xiang et al.
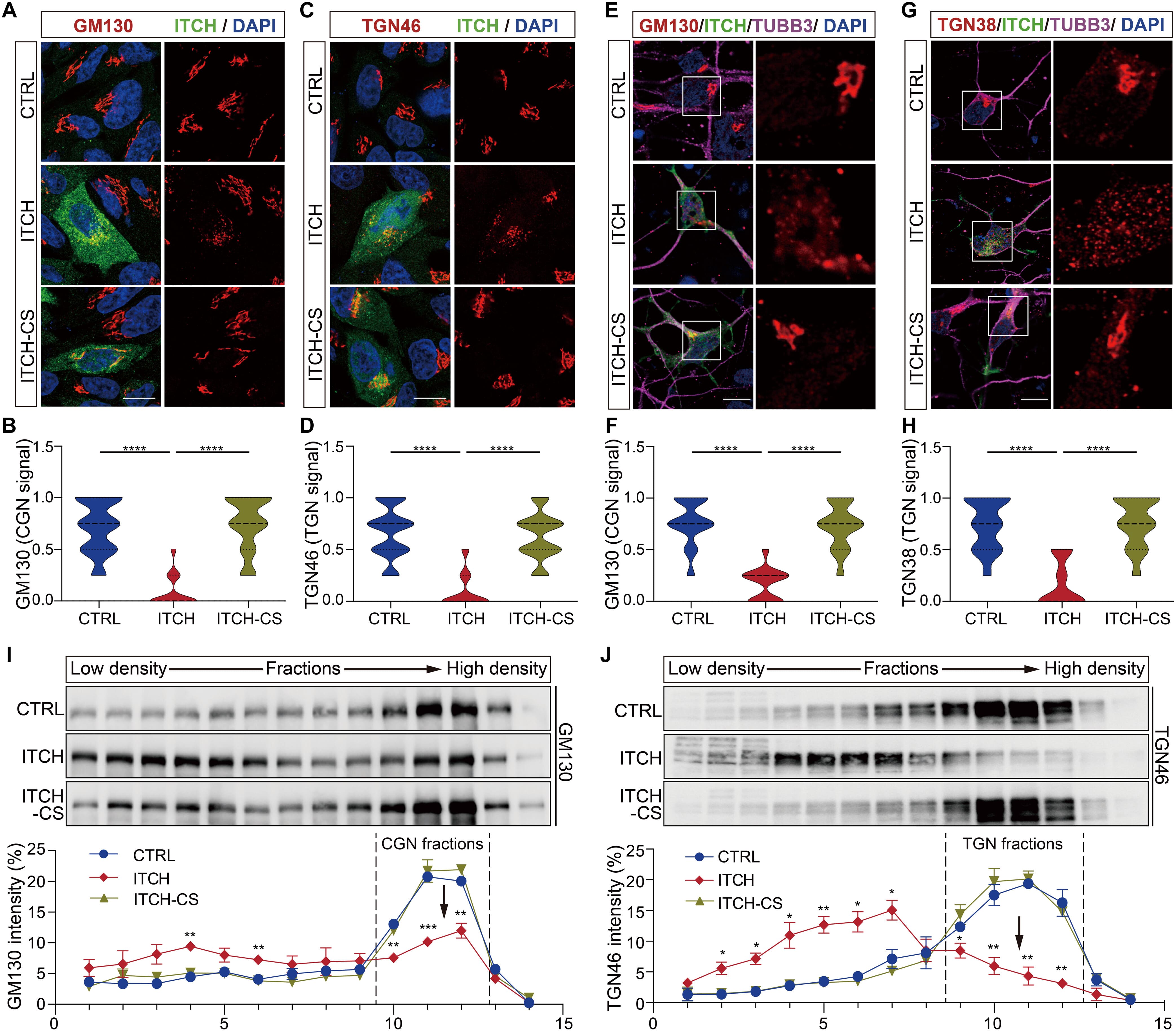
They identified the E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase ITCH as a critical driver of Golgi fragmentation, a recognized early and common feature of neurodegenerative diseases such as Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) and Alzheimer’s Disease (AD). Disease-associated accumulation of ITCH promotes fragmentation of the Golgi, which disrupts protein sorting and impairs crucial lysosomal functions. This dysfunction compromises the clearance of misfolded proteins, contributing significantly to proteotoxicity.
Congratulations to all authors for this great article.
The study demonstrates that inhibiting ITCH offers neuroprotection against misfolded protein-induced toxicity in both mammalian neurons and Drosophila models. To successfully introduce DNA plasmids into sensitive mouse primary cortical neurons, the researchers employed the NeuroMag transfection reagent. This approach confirmed that ITCH induces profound Golgi fragmentation in neuronal cells. These findings underscore the USP11-ITCH axis as a compelling new target for therapeutic development in neurodegeneration.