BLOG > Publications & Citations > Oligomerised RIPK1 is the main core component of the CD95 necrosome
Authors: Nikita V Ivanisenko et al
Source: EMBO J (2025)
We are thrilled to share insights from a recent study entitled "Oligomerised RIPK1 is the main core component of the CD95 necrosome" published in The EMBO Journal by Nikita V Ivanisenko et al:
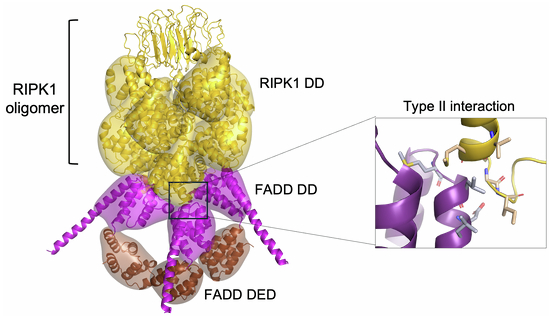
"The necrosome is the key macromolecular signaling platform initiating necroptosis, i.e., a RIPK1/RIPK3-dependent program of cell death with an important role in the control of inflammation in multicellular organisms. However, the composition and structure of the necrosome remain incompletely understood. Here we use biochemical assays, quantitative mass spectrometry, and AlphaFold modeling to decipher the composition and derive a structural model of the CD95L/BV6-induced necrosome. We identify RIPK1 as the central component of the necrosome, forming the core of this complex. In addition, AlphaFold modeling provides insights into the structural mechanisms underlying RIPK1 oligomerization, highlighting the critical role of type-II interactions between the Death Domains (DDs) of FADD and RIPK1 in the assembly of RIPK1-mediated complexes. The role of type-II DD interactions in necroptosis induction is further validated through structure-guided site-directed mutagenesis. Our findings could be useful for the pharmacological targeting of the necroptosis network to treat diseases associated with dysregulated cell death and inflammation."
Congratulations to all authors for this great article.
Our DreamFect Gold was used to transfect DNA in Hela cells.
Read the article See our DreamFect Gold