BLOG > Publications & Citations > A comparative study of cationic lipid-enriched LNPs for mRNA vaccine delivery
Authors: Burcu Binici et al.
Source: International Journal of Pharmaceutics, Volume 682, 2025, 125941, ISSN 0378-5173.
We're delighted to share insights from a significant new publication entitled "A comparative study of cationic lipid-enriched LNPs for mRNA vaccine delivery" published in the International Journal of Pharmaceutics by Burcu Binici et al:
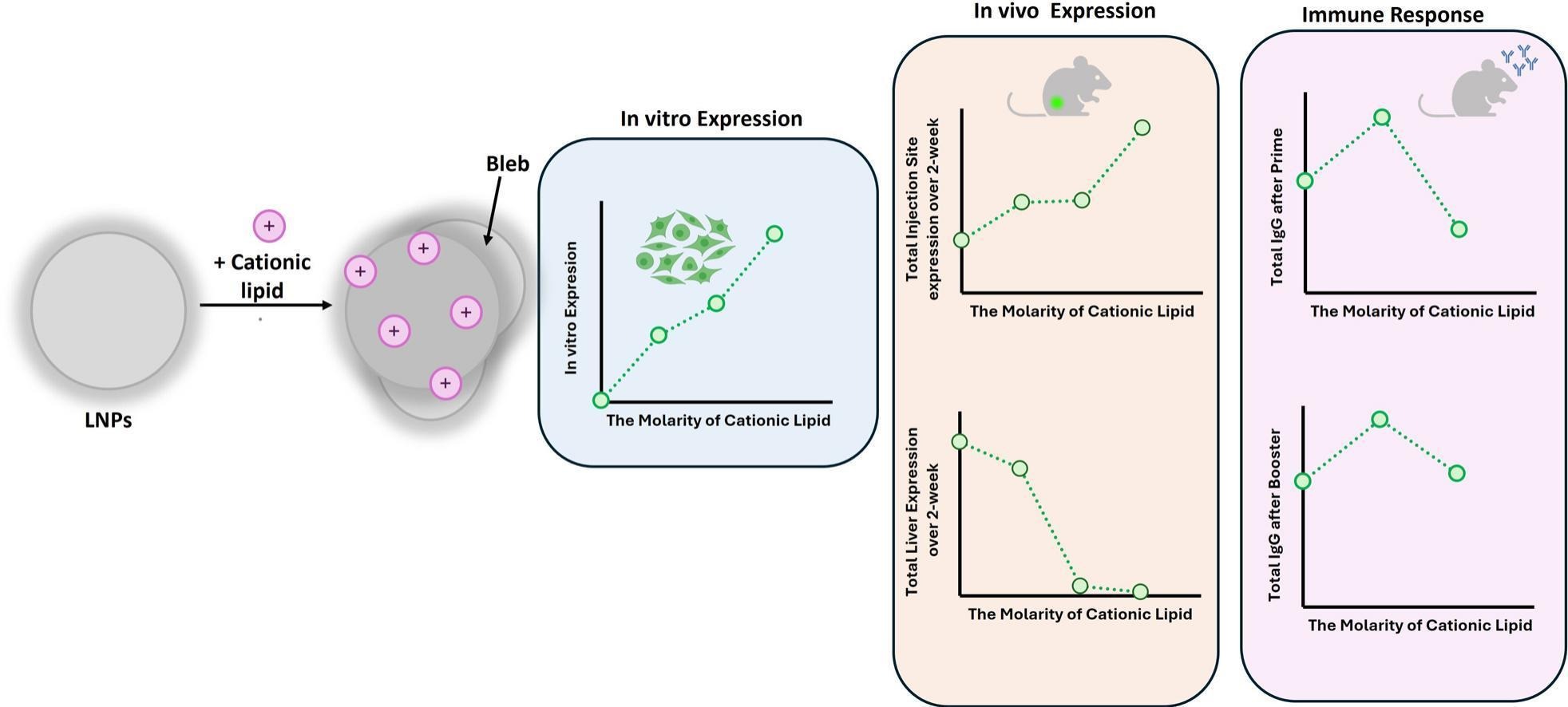
"Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) play a central role in mRNA vaccine delivery; however, intramuscular (IM) administration may lead to off-target hepatic expression. Here, we tested whether incorporating a cationic lipid (DOTAP) into ALC-0315-based LNPs could enhance local mRNA expression and immunogenicity. We used DODAP as a comparable ionisable lipid to DOTAP. LNPs were formulated by partially replacing their ionisable lipid (ALC-0315) with 5–50% DOTAP or 10–50% DODAP and evaluated for their physicochemical characteristics, in vitro transfection efficiency, in vivo expression and immunogenicity in mice. Substituting ALC-0315 with 10–25% DODAP had minimal impact on LNP physicochemical properties and expression both in vitro and in vivo. However, completely replacing ALC-0315 with DODAP reduced LNP potency in vivo. Incorporation of DOTAP into the LNPs shifted the zeta potential to positive values and altered morphology, with 5–25% DOTAP increasing in vitro transfection efficiency and enhancing local protein expression at the injection site. Notably, 10% DOTAP reduced hepatic expression, suggesting improved localised expression. Immunisation studies with OVA mRNA-LNPs demonstrated that 5% DOTAP enhanced total IgG responses after the prime dose, whereas higher DOTAP or DODAP levels produced minimal differences or reduced responses; these differences were not sustained after booster immunisation, providing no significant long-term benefits."
Congratulations to all the authors on this excellent article!
Authors effectively utilized our Ovalbumin (OVA)-encoding mRNA, modified with 5-methoxyuridine, for comprehensive in vivo immunization studies.
Read the article See our OVA mRNA