BLOG > Publications & Citations > Human CD4 T cells are functional targets for LNP-based mRNA vaccines
Authors: Kim SC, et al.
Source: mBio 0:e02254-25.
We're delighted to share insights from a groundbreaking study entitled "Human CD4 T cells are a functional target for lipid nanoparticle-based mRNA vaccines" published in mBio by Samuel C. Kim et al.
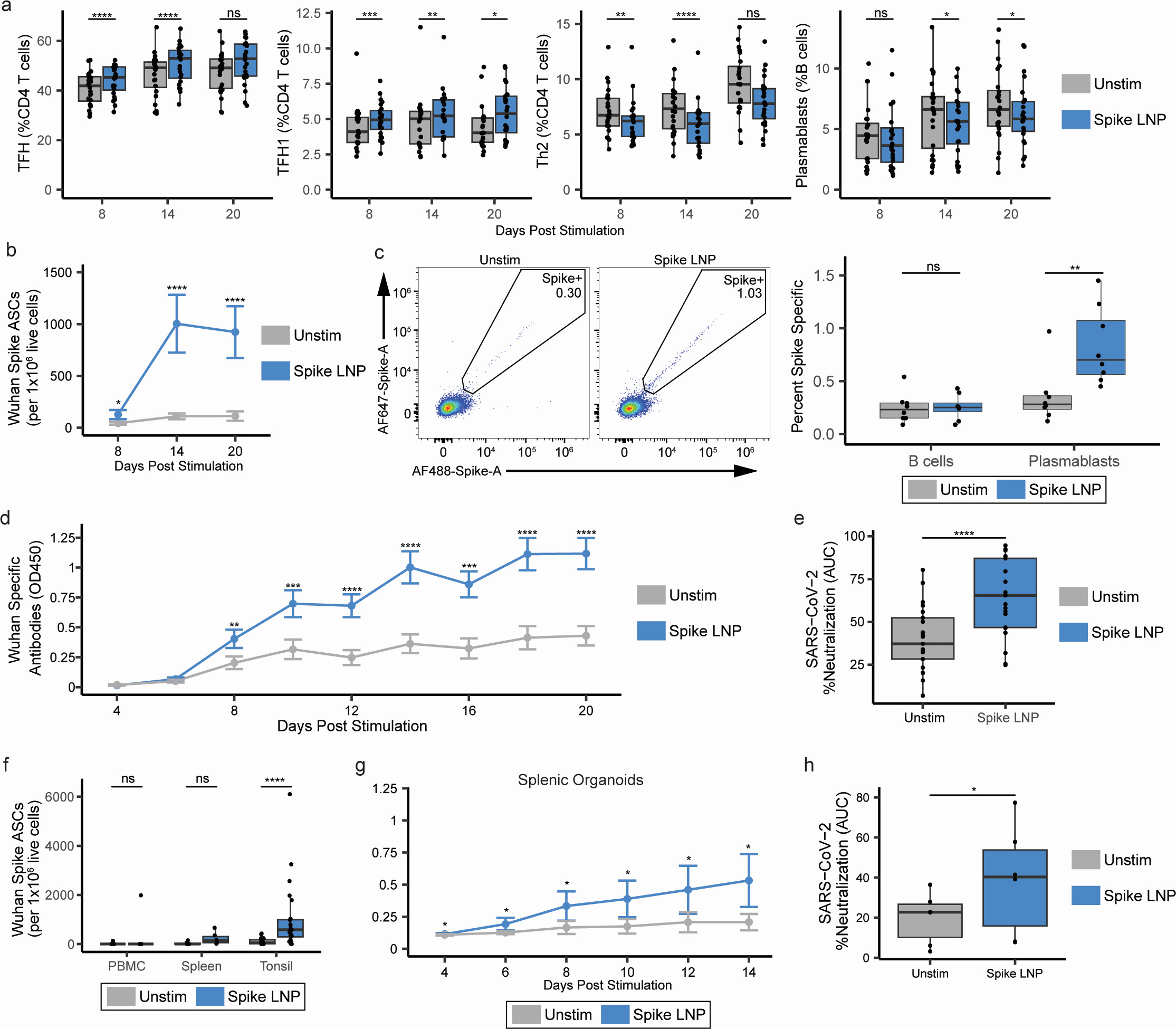
They discovered that CD4 T cells are an unexpected and dominant target for lipid nanoparticle (LNP) transfection, both in human lymphoid organoids and in a murine immunization model. These CD4 T cells efficiently express the encoded protein, representing a significant source of antigen production after mRNA LNP immunization. Furthermore, the researchers showed that protein production from CD4 T cells alone is sufficient to support robust humoral (antibody) responses to the SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine. This critical finding suggests that non-antigen-presenting immune cells can support effective adaptive immunity, opening doors to new vaccination strategies.
Congratulations to all the authors on this excellent article!
Our SARS CoV-2 Spike mRNA was utilized in this work to study LNP distribution and adaptive immunity mechanisms.
Read the article SARS CoV-2 Spike mRNA