BLOG > Publications & Citations > Lymphoid gene expression supports neuroprotective microglia function
Authors: Ayata, P., Crowley, J.M., Challman, M.F. et al.
Source: Nature 648, 157–165 (2025).
We're delighted to share insights from a genuine study entitled "Lymphoid gene expression supports neuroprotective microglia function" published in Nature by Pinar Ayata et al:
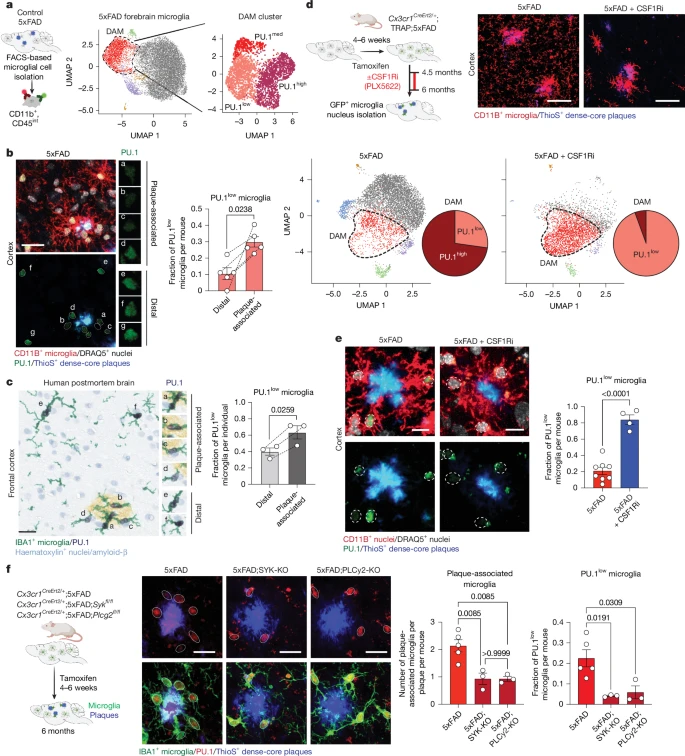
They discovered that the protective function of microglia, the brain’s innate immune cells, against Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is governed by reduced expression of the transcription factor PU.1. When PU.1 levels are lowered, microglia adopt a neuroprotective phenotype expressing lymphoid receptor proteins, such as CD28. This cellular shift mitigates neuroinflammation, reduces amyloid pathology, and preserves synaptic function, significantly extending the lifespan of AD model mice. This exciting finding points toward novel immunotherapy approaches for AD by promoting these protective microglial functions.
Congratulations to all the authors on this excellent article!
Our Glial-Mag Transfection Reagent was used to successfully introduce siRNAs for acute PU.1 knockdown in primary mouse microglia. This efficient in vitro technique confirmed that reducing PU.1 expression is sufficient to induce the rapid transcriptional shift toward lymphoid-associated gene expression in microglia.
Read the article See our Glial-Mag