BLOG > Publications & Citations > Uukuniemi virus infection remodels the RNA-binding proteome in tick cells
Authors: Wilson A, Kamel W, Davies K, De Laurent ZR, Arif R, et al.
Source: PLOS Pathogens 21(8): e1013393.
We are delighted to share insights from a recent study entitled "Uukuniemi virus infection causes a pervasive remodelling of the RNA-binding proteome in tick cells" published in PLoS Pathogens by Alexandra Wilson et al.
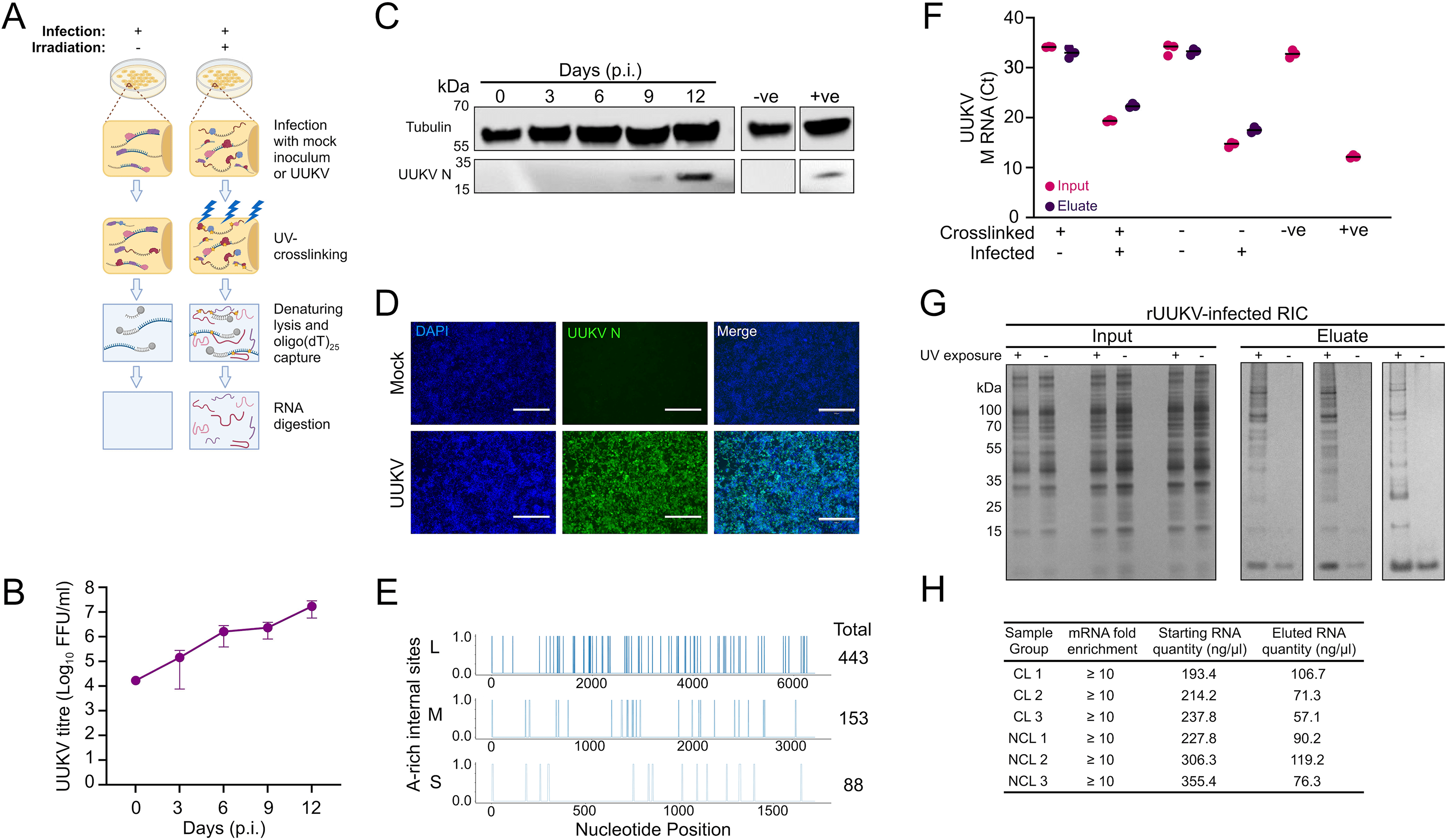
They conducted the first comprehensive analysis of protein-RNA interactions in Uukuniemi virus-infected tick cells, revealing a widespread remodeling of the RNA-binding proteome and identifying 283 proteins with altered RNA-binding activity. Their work highlighted the tick homolog of topoisomerase 3B (TOP3B) as a key host factor impacting viral particle production.
Congratulations to all authors for this great article.
Our Magnetofectamine O2 was used to facilitate the optimized delivery of dsRNA into tick cells. This enabled the researchers to effectively knock down candidate RNA-binding proteins, validating their significant roles in UUKV infection and demonstrating the specificity and efficacy of their approach.
Read the article Check Magnetofectamine O2