BLOG > Publications & Citations > Meningococci drive host membrane tubulation to recruit their signaling receptors
Authors: Laurent-Granger, A., Sollier, K., Saubamea, B. et al.
Source: Nat Commun 16, 10433 (2025).
We're delighted to share insights from a recent study entitled "Meningococci drive host membrane tubulation to recruit their signaling receptors" published in Nature Communications by Audrey Laurent-Granger, Kévin Sollier et al:
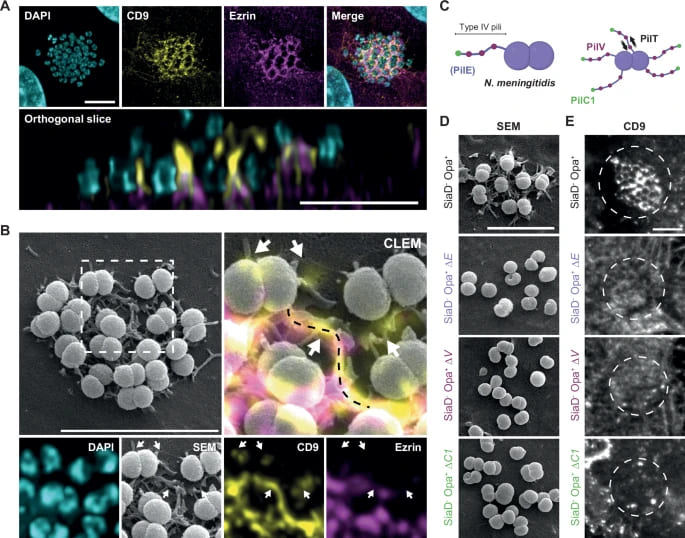
They uncovered a crucial survival strategy utilized by Neisseria meningitidis (meningococci) to rapidly interact with host cells, despite the constraints of circulating in the bloodstream. They report that meningococcal Type IV pili (T4P) exploit the physical dynamics of the host plasma membrane to trigger the formation of early tubular membrane structures (TMS). This physical process, independent of host cell signaling, concentrates critical plasma membrane-associated proteins and signaling receptors near the bacteria. This local enrichment dramatically increases the probability of ligand-receptor interactions, which is essential for initiating host cell signaling and stabilizing bacterial colonization.
Congratulations to all the authors on this excellent article!
Our EcoTransfect was used to transfect HEK cells with plasmids, including those encoding hCEACAM and YFP-CD9, necessary for studying receptor accumulation and signaling in cells incompetent for typical meningococcal infection.
Read the article See EcoTransfect