BLOG > Publications & Citations > New publication: Local magnetic delivery of adeno-associated virus AAV2
Authors: Mukherjee, Subhendu et al.
Source: Molecular Therapy, Volume 30, Issue 2, 519 - 533
We are thrilled to share insights from a study titled "Local magnetic delivery of adeno-associated virus AAV2(quad Y-F)-mediated BDNF gene therapy restores hearing after noise injury" published in Molecular Therapy by Mukherjee, Subhendu et al.
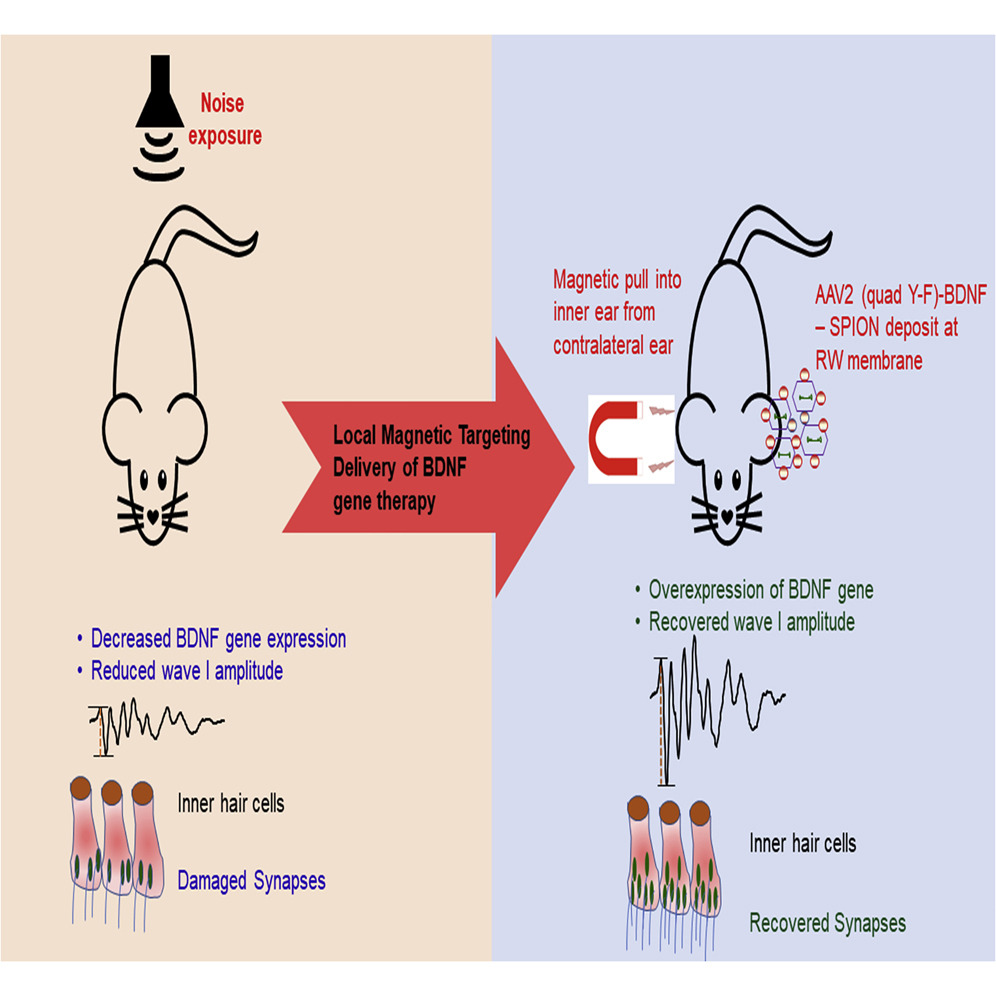
"Moderate noise exposure may cause acute loss of cochlear synapses without affecting the cochlear hair cells and hearing threshold; thus, it remains “hidden” to standard clinical tests. This cochlear synaptopathy is one of the main pathologies of noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL). There is no effective treatment for NIHL, mainly because of the lack of a proper drug-delivery technique. We hypothesized that local magnetic delivery of gene therapy into the inner ear could be beneficial for NIHL. In this study, we used superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) and a recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector (AAV2(quad Y-F)) to deliver brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene therapy into the rat inner ear via minimally invasive magnetic targeting. We found that the magnetic targeting effectively accumulates and distributes the SPION-tagged AAV2(quad Y-F)-BDNF vector into the inner ear. We also found that AAV2(quad Y-F) efficiently transfects cochlear hair cells and enhances BDNF gene expression. Enhanced BDNF gene expression substantially recovers noise-induced BDNF gene downregulation, auditory brainstem response (ABR) wave I amplitude reduction, and synapse loss. These results suggest that magnetic targeting of AAV2(quad Y-F)-mediated BDNF gene therapy could reverse cochlear synaptopathy after NIHL."
Congratulations to all authors for this great article.
Our Mag4C-AD was used to capture and magnetically locally deliver adeno-associated virus AAV2 in vivo.
Read the paper See our Mag4C-AD