BLOG > mRNA & LNP > mRNA and LNPs: A Guide to Fluorescent Labeling to Enhance Research

Summary:
1. Understanding mRNA and LNP fluorescent labeling
2. Overview of fluorescent labeling techniques for mRNA and LNPs
3. Fluorescent mRNAs for tracking expression
4. Fluorescent LNPs: visualizing delivery systems
5. Choosing the right fluorescent labels for mRNA or LNP
6. Best practices for fluorescent labeling in mRNA and LNP research
In the context of nucleic acid delivery and molecular biology research, the ability to fluorescently label messenger RNA (mRNA) and lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) is extremely useful for analyzing their behavior in biological systems. Here, we discuss on the principles and techniques of fluorescent labeling for mRNA and LNPs, with an emphasis on their applications in research.
1. Understanding mRNA and LNP fluorescent labeling
By covalently attaching or incorporating fluorophores into these molecules or delivery systems, fluorescent labeling enables easy visualization and tracking of mRNA molecules and LNP formulations in vitro and in vivo, in real time.
This allows characterizing delivery mechanisms, cellular uptake and assessing transfection efficiency. Additionally, fluorescence labeling facilitates the study of biodistribution in vivo. For researchers working with complex delivery systems, these tools provide essential quantitative and qualitative data.
2. Overview of fluorescent labeling techniques for mRNA and LNPs
Depending on the target molecule and research objective, several labeling strategies can be employed:
- Covalent fluorophore conjugation: for mRNA, fluorescent dyes like Alexa Fluor, Cy dyes, or the more chemically stable Atto dyes can be covalently attached. This is typically achieved through reactive groups on the dye that form stable bonds with functional groups on modified nucleotides. This approach ensures stable labeling and is widely used for tracking synthetic mRNA or lipid-based delivery systems.
- Incorporation of fluorescent analogs during synthesis: particularly for nucleic acids, allows integration of fluorophore-modified nucleotides directly during in vitro transcription. This method preserves mRNA integrity and translation capability while enabling direct fluorescence detection.
- Lipid-based fluorescent tagging: commonly used for nanoparticles, involves the incorporation of lipophilic fluorescent dyes (e.g., DiI, DiD,DiR, DiO… or rhodamine derivatives) into lipid membranes during formulation without disrupting the nanoparticle's structure. These dyes capitalize on their hydrophobic nature to associate with lipid components. This technique provides robust signal intensity and is compatible with live-cell imaging and biodistribution studies.
- Indirect labeling: through the use of fluorescently labeled probes or antibodies, is less common for mRNA or LNPs due to specificity and delivery constraints, but may be used in fixed samples or downstream detection workflows.
3. Fluorescent mRNAs for tracking expression
OZ Biosciences fluorescent mRNAs have been designed to produce high expression level of a reporter gene. They can be used as control of transfection efficiency.
When labeled with fluorescent agent, those mRNA can be easily traced to analyze mRNA delivery and translation efficiency.
Produced by in vitro transcription, incorporating 5’ cap structures (Cap 1) and poly(A) tails to mimic mature eukaryotic transcripts. These modifications enhance stability and performance.

Figure 1: Example of the structure of a fluorescent mRNA, here a (5moU/U-Cy5).
Our Fluorescent mRNA products:
We offer mRNAs fluorescently labeled with Cy5, Cy3, or AlexaFluor488, targeting high expression of either Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) or Firefly Luciferase (F-Luc). These mRNAs are easily traced to analyze mRNA delivery and translation efficiency.
GFP mRNA: Designed to produce high expression level of Green Fluorescent Protein. Available on:
- Cy5 GFP mRNA (labeled with Cy5).
- Cy3 GFP mRNA (labelled with Cy3 by replacing 15 % of UTP by UTP-Cy3).
F-Luc mRNA: Designed to produce high expression level of FireFly Luciferase Protein. Available on:
- Cy5 F-Luc mRNA (labeled with Cy5).
- Cy3 F-Luc mRNA (labelled with Cy3 by replacing 15 % of UTP by UTP-Cy3).
- Alexa488 F-Luc mRNA (labelled with AlexaFluor488 by replacing 15 % of UTP by UTP-AF488).
All our fluorescent mRNAs are available in three vairants: Unmodified, 5moU or N1-mψ.
4. Fluorescent LNPs: visualizing delivery systems
Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) represent one of the most effective and safe delivery systems for the translational success of nucleic acid drugs. LNPs are lipidic spherical vesicles formed by a combination of four main components: an ionizable cationic lipid, a helper phospholipid, cholesterol & a pegylated lipid, each having distinct functions. LNPs not only protect RNA from degradation, but also facilitate intracellular uptake and thus potentiate its efficacy.
By incorporating fluorescent lipophilic dyes into their structure, LNPs can be tracked during cellular internalization and systemic biodistribution studies.
At OZ Biosciences, we have developed a range of fluorescent LNPs called NanOZ Fluo LNP.
Our NanOZ Fluo LNPs are designed for the effective monitoring and imaging of intracellular trafficking and biodistribution of LNPs in vitro and in vivo respectively.
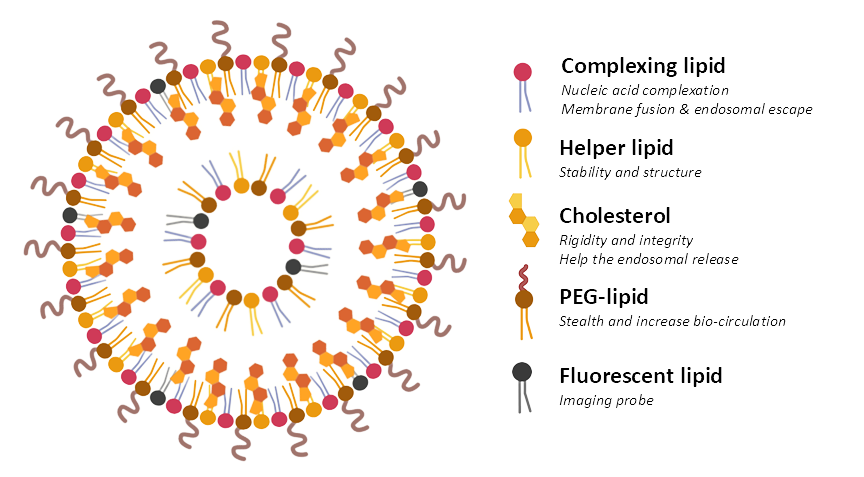
Figure 2: Schematic representation of fluorescent LNPs.
Our fluorescent LNP products:
We offer ready-to-use LNPs fluorescently labeled with DiR, DiO, or Dil for in vitro cellular and subcellular distribution and in vivo imaging:
- NanOZ Fluo LNP-DiR: contains a lipophilic carbocyanine dye DiR having an excitation max. at 748 nm, and emission max. at 780 nm.
- NanOZ Fluo LNP-DiO: contains a lipophilic carbocyanine dye DiO having an excitation max. at 487 nm, and emission max. at 501 nm.
- NanOZ Fluo LNP-DiI: contains a lipophilic carbocyanine dye DiI having an excitation max. at 549 nm, and emission max. at 565 nm.
- NanOZ Dual Fluo LNP-DiO/Cy5-mRNA F-Luc: contains a lipophilic carbocyanine dye DiO having an excitation max. at 487 nm, and emission max. at 501 nm and Cy5 mRNA having excitation max. at 651 nm, and emission max. at 670 nm.
5. Choosing the right fluorescent labels for mRNA or LNP
When selecting a fluorescent probe for labeling mRNA or LNPs, we recommend considering the following points:
- Spectral properties: Ensure compatibility with imaging system filters.
- Photostability: For time-lapse or long-term imaging.
- Toxicity: Prefer non-cytotoxic dyes.
- Size and charge: Especially relevant for LNP formulation integrity.
6. Best practices for fluorescent labeling in mRNA and LNP research
To ensure data accuracy and reproducibility, we recommend:
- Optimize concentration and incubation conditions.
- Include appropriate positive and negative controls.
- Minimize photobleaching with antifade reagents or low-light acquisition.
- For mRNA: we recommend using our transfection reagents RmesFect or RmesFect Stem in order to reach high transfection efficiency and optimum protein expression level.
- For LNP: Adjust volume depending on the plate format and desired LNPs concentration.
- Don’t hesitate to check scientific publications and specialized journals that provide detailed information on fluorescent labeling techniques and their applications in mRNA and LNP research.
- And of course, follow the protocol provided with the product!
To learn more about fluorescent mRNA & LNP, take a look at our other ressources and discover our products: